- با ما در تماس باشید
- 09308658811
- iranepf@gmail.com
Moderate aerobic exercise training decreases middle-aged induced pathologic cardiac hypertrophy by improving Klotho expression, MAPK signaling pathway and oxidative stress status in Wistar rats
تأثیر هشت هفته تمرین پیلاتس بر سطوح سرمی اورکسین و مقاومت به انسولین در کودکان دارای اضافهوزن
۷ مرداد ۱۳۹۷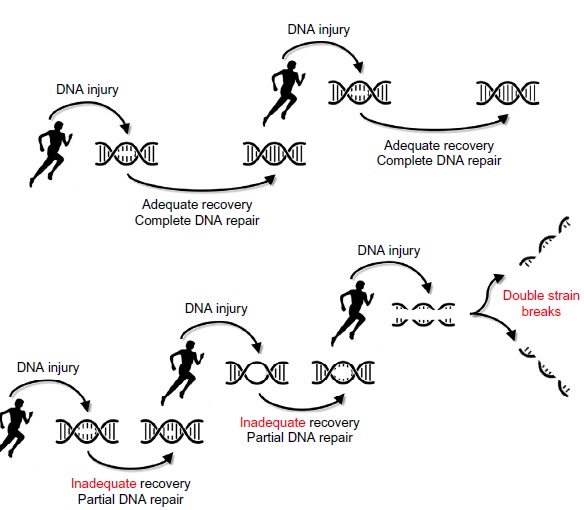
ورزش و آسیب های DNA
۳۱ مرداد ۱۳۹۷Behrouz Baghaiee 1; Pouran Karimi1; Marefat Siahkouhian2; Linda S Pescatello3
The Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences (IJBMS)
Objective(s): This study aimed to investigate the effect of aerobic training on serum levels of Klotho, cardiac tissue levels of H2O2 and phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and P38 as well as left ventricular internal diameter (LVID), the left ventricle wall thickness (LVWT) and fibrosis in middle-aged rats.
Materials and Methods: Forty wistar rats, including young rats (n=10, 4 month-old) and middle-aged rats (n=30, 13-15 months-old) were enrolled in this experimental study. The all young and 10 middle-aged rats were sacrificed (randomly) under deep anesthesia without any exercise training as normal young control and normal middle-aged control respectively. The remaining 20 middle-aged rats participated in 4 (n=10) or 8-week (n=10) aerobic exercise training.
Results: There were significant differences in the plasmatic Klotho levels and the heart tissue levels of phosphorylated-ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2), P-P38 and H2O2, LVWT, LVID and fibrosis between young and middle-aged rats (P=0.01). Plasmatic Klotho level was significantly increased after eight weeks training (P=0.011). Also, p-ERK1/2 was significantly decreased after eight weeks and p-P38 was significantly decreased in the fourth (P=0.01) and eight weeks of training (P=0.01). A similar decrease was reported for aging-induced H2O2 in the fourth (P=0.016) and eighth weeks (P=0.001). LVID was significantly increased in eight weeks, but LVWT and fibrosis was significantly reduced in the eighth week (P=0.011, P=0.028, P=0.001 respectively).
Conclusion: Moderate aerobic training attenuates aging-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy at least partially by restoring the Klotho levels, attenuating oxidative stress, and reduction in the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, P38 and fibrosis.
Keywords
Exercise; Fibrosis; H2O2; Left ventricular hypertrophy; Klotho; Mitogen-activated protein; kinase